Phishing attacks rely on browser parasites. – Phishing attacks rely on browser parasites, a sinister alliance that poses a significant threat to cybersecurity. These parasites, insidious in nature, exploit vulnerabilities in web browsers to facilitate phishing scams, compromising user security and causing widespread damage.
Browser parasites, often masquerading as legitimate browser extensions or plugins, lurk in the shadows, silently monitoring user activity and harvesting sensitive information. They can redirect users to malicious websites, inject fraudulent content into legitimate sites, and even steal login credentials, giving attackers a gateway to personal accounts and financial data.
Browser Parasites and Phishing Attacks
Browser parasites are malicious software that attach themselves to web browsers and alter their behavior. They can be used to facilitate phishing attacks, which attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information by disguising themselves as legitimate websites.
Browser parasites can inject malicious code into web pages, redirect users to phishing sites, and steal sensitive data entered into forms.
Common Browser Parasites Used in Phishing Campaigns
- Adware: Displays unwanted advertisements on web pages.
- Spyware: Collects user data, such as browsing history and keystrokes.
- Keyloggers: Records every keystroke made on the computer.
- Browser hijackers: Change browser settings, such as the homepage and search engine.
Browser parasites can significantly impact user security by compromising their privacy and exposing them to financial fraud and identity theft.
Detection and Prevention of Browser Parasites
Methods for Detecting Browser Parasites
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software to scan the computer.
- Check for suspicious browser extensions or plugins.
- Examine the browser’s settings for any unusual changes.
- Monitor the computer’s network traffic for suspicious activity.
How to Remove Browser Parasites, Phishing attacks rely on browser parasites.
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software to remove the parasite.
- Manually remove suspicious browser extensions or plugins.
- Reset the browser’s settings to their default values.
- Scan the computer’s network traffic for suspicious activity and block any malicious connections.
Tips for Preventing Browser Parasite Infections
- Keep software and browsers up to date with the latest security patches.
- Be cautious when installing browser extensions or plugins.
- Use a reputable antivirus and anti-malware program.
- Be aware of phishing scams and avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments.
Case Studies of Phishing Attacks

Case Study 1: The Gmail Phishing Attack
In 2021, a phishing campaign targeted Gmail users with emails that appeared to come from Google. The emails contained a link to a fake login page that stole users’ credentials.
The attack was successful because the phishing emails were well-crafted and the fake login page was nearly identical to the real one.
Lessons learned: Be cautious when clicking on links in emails, even if they appear to come from legitimate sources.
Case Study 2: The Amazon Prime Phishing Attack
In 2022, a phishing campaign targeted Amazon Prime users with emails that offered a free subscription. The emails contained a link to a fake website that stole users’ payment information.
The attack was successful because the phishing emails were persuasive and the fake website looked authentic.
Lessons learned: Be wary of offers that seem too good to be true and check the URL of any website before entering sensitive information.
Emerging Trends in Phishing Attacks: Phishing Attacks Rely On Browser Parasites.

Trend 1: Increased Use of Browser Parasites
Phishing attacks are increasingly using browser parasites to facilitate their attacks. Browser parasites can make phishing websites more convincing and bypass security measures.
Trend 2: Targeted Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are becoming more targeted, with attackers focusing on specific individuals or organizations. This makes phishing emails more personalized and difficult to detect.
Trend 3: Use of Social Media
Phishing attacks are increasingly using social media to spread their messages. This allows attackers to reach a wider audience and target specific groups of people.
Trend 4: Mobile Phishing
Phishing attacks are also becoming more common on mobile devices. This is because mobile devices are often used to access sensitive information, such as banking and email accounts.
Browser Parasite Mitigation Strategies
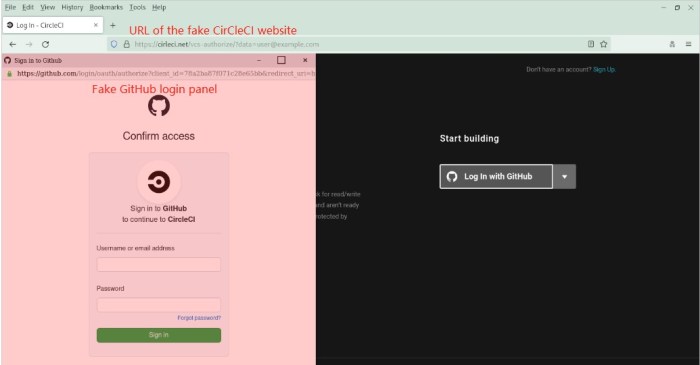
Comprehensive Strategy for Mitigating Browser Parasite Threats
A comprehensive strategy for mitigating browser parasite threats should include the following elements:
- Use a reputable antivirus and anti-malware program.
- Keep software and browsers up to date with the latest security patches.
- Be cautious when installing browser extensions or plugins.
- Be aware of phishing scams and avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments.
- Use a browser that has built-in security features, such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
- Educate users about browser parasite threats and how to avoid them.
Table of Mitigation Techniques and Effectiveness
| Mitigation Technique | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Use a reputable antivirus and anti-malware program | High |
| Keep software and browsers up to date with the latest security patches | Medium |
| Be cautious when installing browser extensions or plugins | Medium |
| Be aware of phishing scams and avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments | Low |
| Use a browser that has built-in security features | High |
| Educate users about browser parasite threats and how to avoid them | Medium |
Top FAQs
How do browser parasites facilitate phishing attacks?
Browser parasites can inject malicious code into web pages, redirect users to phishing sites, and steal login credentials, aiding attackers in their phishing campaigns.
What are some common examples of browser parasites used in phishing?
Adware, spyware, keyloggers, and rogue browser extensions are common types of browser parasites employed in phishing attacks.
How can I detect and remove browser parasites?
Regularly scanning your system with reputable antivirus software, checking browser extensions for suspicious activity, and resetting browser settings can help detect and remove browser parasites.
What are the best practices to prevent browser parasite infections?
Installing ad blockers, being cautious of unsolicited browser extensions, and keeping software up to date can help prevent browser parasite infections.