Exercise 29 us geological survey topographic maps – Embarking on Exercise 29: Analyzing USGS Topographic Maps, we delve into the fascinating world of cartography, where maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the intricacies of our planet’s terrain. These maps, meticulously crafted by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), provide a comprehensive representation of Earth’s surface, enabling us to decipher the topography, elevation, and various features that shape our landscapes.
Through this exercise, we will embark on a journey to unravel the secrets hidden within these maps, learning how to interpret contour lines, decipher symbols, and extract valuable information about the physical characteristics of the land. By the end of this exploration, we will gain a newfound appreciation for the power of topographic maps and their indispensable role in fields ranging from land use planning to environmental assessment and outdoor recreation.
Introduction
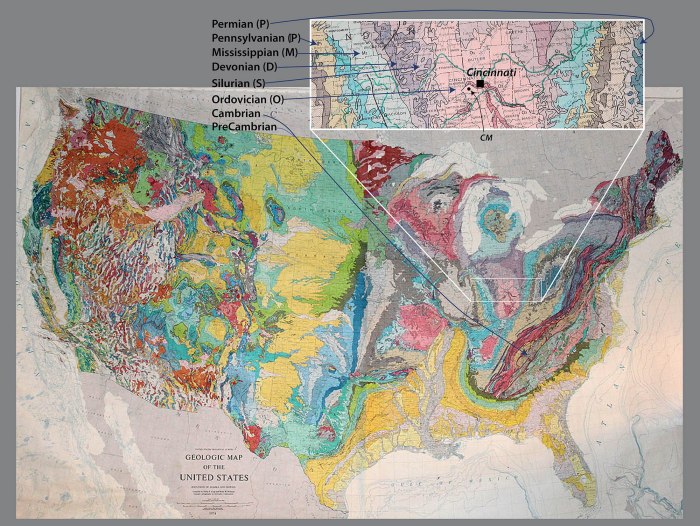
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) topographic maps are detailed representations of the Earth’s surface. These maps provide valuable information about the topography, elevation, and other physical features of a particular area. They serve as essential tools for a wide range of applications, including land use planning, environmental assessment, and recreational activities.
Understanding Topographic Maps: Exercise 29 Us Geological Survey Topographic Maps
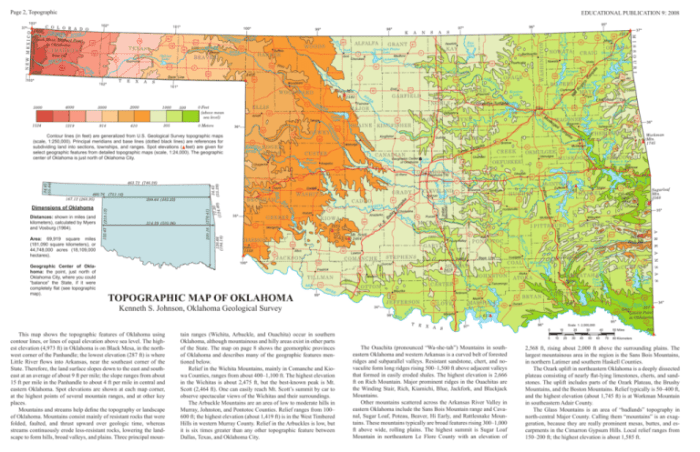
Topographic maps use contour lines to depict the elevation and shape of the land. Each contour line represents a specific elevation above or below a reference point, typically sea level. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope of the land.
Topographic maps also include symbols to represent various features, such as roads, rivers, and vegetation.
Exercise 29: Analyzing Topographic Maps, Exercise 29 us geological survey topographic maps
Exercise 29 focuses on analyzing USGS topographic maps to understand the terrain and landscape. The objectives of this exercise are to:
- Identify and interpret contour lines to determine elevation and slope.
- Use map symbols to locate and analyze features such as roads, rivers, and vegetation.
- Develop an understanding of the relationship between topography and drainage patterns.
Map Features and Analysis
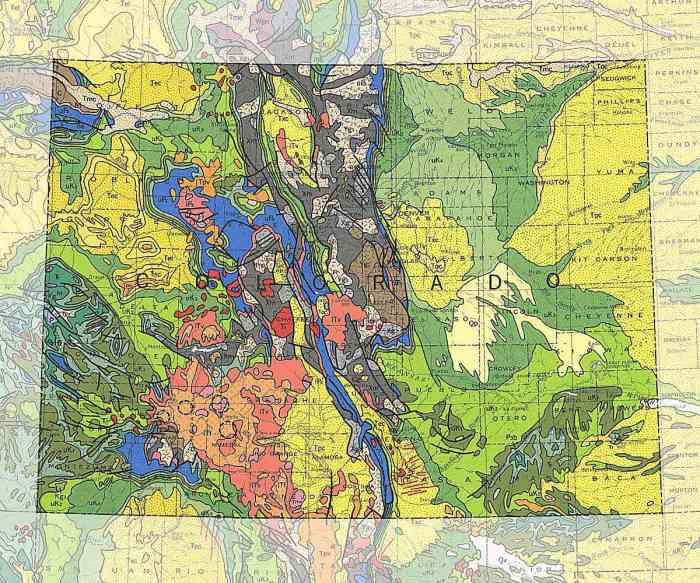
USGS topographic maps contain various features that provide information about the terrain and landscape. These features include:
- Elevation:Contour lines represent the elevation of the land, with each line indicating a specific height above or below a reference point.
- Slope:The spacing of contour lines indicates the slope of the land. Closely spaced contour lines represent steep slopes, while widely spaced contour lines indicate gentle slopes.
- Drainage Patterns:Rivers, streams, and other water bodies are depicted on topographic maps using blue lines. The pattern of these water bodies can provide insights into the topography and hydrology of the area.
- Vegetation:Green areas on topographic maps represent vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands. The type and density of vegetation can influence the terrain and affect land use.
Applications of Topographic Maps
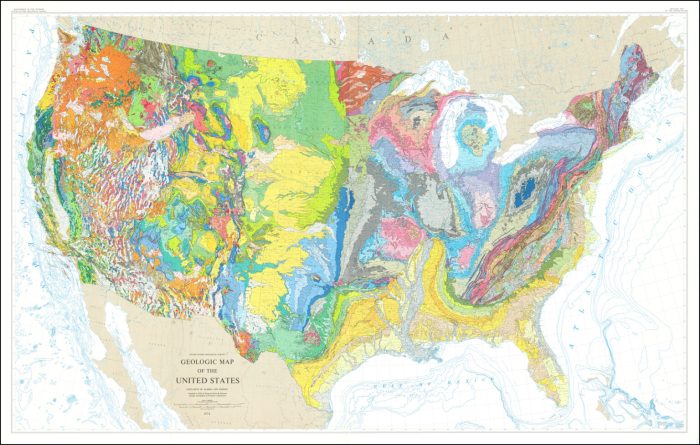
Topographic maps have a wide range of applications, including:
- Land Use Planning:Topographic maps provide valuable information for land use planning, as they depict the topography, slope, and other physical features of an area.
- Environmental Assessment:Topographic maps can be used to assess environmental impacts, such as erosion, flooding, and habitat loss.
- Recreation and Outdoor Activities:Topographic maps are essential for planning and navigating outdoor activities, such as hiking, camping, and hunting.
General Inquiries
What are the key features of USGS topographic maps?
USGS topographic maps are characterized by contour lines, which depict elevation changes, as well as symbols representing various natural and man-made features, such as roads, rivers, and vegetation.
How can I determine the elevation of a point on a topographic map?
Elevation is indicated by contour lines, with each line representing a specific elevation value. By interpolating between contour lines, you can estimate the elevation of any point on the map.
What is the purpose of scale on a topographic map?
The scale provides a ratio between the map and the actual ground distance, allowing you to determine the real-world dimensions of features on the map.